Did you know that in 2022, the United States faced approximately 480,000 cyberattacks? These alarming statistics emphasize the critical need for secure websites that safeguard sensitive data from malicious threats.
When a website is compromised or offline, businesses can lose millions in revenue as customers cannot access their services. Beyond financial losses, such incidents can severely damage a company’s reputation. To reduce these risks, deploying a proxy server is a smart solution.
In this guide, we’ll explore proxy servers, how they work, their types, benefits, and the setup process.
In 2023, the global proxy server market was valued at approximately USD 3.4 billion.
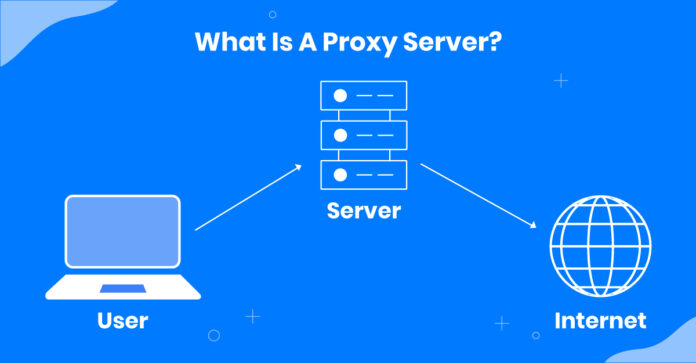
What is a Proxy Server?
A proxy server is a system or router that acts as a gateway between users and the internet, helping to protect private networks from cyberattacks. Often referred to as an “intermediary,” it sits between end-users and the websites they access online.
When a proxy server is used, internet traffic is routed through the proxy before reaching the destination server. Because all communication passes through the proxy, it provides a layer of security and privacy. Many IT companies rely on proxy servers to filter out potentially harmful data from the internet, ensuring safer and more controlled access to online resources.
This added security is even more effective when combined with a secure web gateway or email security solutions. It allows you to filter traffic based on its safety level or the capacity of your network and individual devices.
How Does a Proxy Server Work?
Step 1: The User Sends a Request for Information
It starts when a user wants to access a website or online resource. They enter a URL in their browser or use an app to request data.
This request includes details like the destination website or service the user wishes to interact with.
Step 2: The Proxy Server Receives the Request
Instead of going straight to the destination website’s server, the request is first sent to the proxy server. Acting as a gatekeeper, the proxy server receives the request from the user’s device, examines the requested content, and determines the most efficient way to process it.
Step 3: The Proxy Server Sends the Request to the Destination Server
Once the proxy server receives your request, it forwards it to the destination server—the website or service you want to access. During this process, the proxy may modify the request by masking your IP address to protect your privacy. As a result, the destination server only sees the proxy’s IP address and not yours.
Step 4: The Destination Server Sends a Response to the Proxy Server
The destination server processes the request and generates a response, such as a webpage or data. It then sends this response back to the proxy server, still unaware of your original IP address or device.
Step 5: The Proxy Server Delivers the Data to the User
Finally, the proxy server forwards the response to your device, allowing you to access the requested content, whether a webpage, video, or file. Throughout this process, the proxy keeps your IP address hidden and can enhance security by adding features like encryption, depending on the proxy type.
Step 6: Modifying Requests and Responses
Proxy servers can alter both requests and responses in various ways to enhance functionality and performance:
-
Caching:
Proxy servers can store frequently accessed content in their cache. When multiple clients request the same content, the proxy can deliver it directly from its cache, improving speed and reducing the load on the origin server.
-
Content Filtering:
These servers can filter content based on predefined rules, such as blocking access to specific websites or advertisements to enhance security or enforce organizational policies.
-
Compression and Optimization:
Some proxy servers compress data or optimize content, ensuring a smoother experience for users with slower internet connections by reducing the size of transmitted data.
Forward proxies and Reverse proxies are among the most widely utilized proxy types.
How to Set Up a Proxy Server in Windows
- Click on the Start menu and search for Settings.
- Choose Network & Internet.
- Click Proxy in the left panel.
- To manually set up a proxy server, go to the Manual Proxy Setup section and toggle the “Use a Proxy Server” option to On. Also, ensure the “Automatically Detect Settings” toggle is turned On.
By default, Windows automatically checks if your organization, school, or local network has a pre-configured proxy server ready. Windows will provide its name and guide you through the setup process if it finds one. - If Windows detects a PAC file (Proxy Auto-Config file), go to the Automatic Proxy Setup section and toggle the “Use Setup Script” option to On to enable it.
- Add the Script address and click on the Save button.
Types of Proxy Server
1. Forward Proxy
A forward proxy is an intermediary between users and the internet, routing requests from internal networks to external resources. It helps maintain privacy and control by managing access to online content.
Ideal for internal networks, it provides security but might limit the ability to cater to individual user needs.
Info: Read more about Forward Proxy vs. Reverse Proxy
2. Transparent Proxy
A transparent proxy works without the user knowing, making it “invisible” during internet browsing. It’s useful for companies that want to use a proxy while keeping it seamless for employees.
However, it’s vulnerable to security threats like denial-of-service attacks.
3. Anonymous Proxy
An anonymous proxy hides the user’s identity when browsing online, ensuring their activity remains untraceable.
It is best for users seeking complete anonymity, although using one may lead to potential scrutiny.
4. High Anonymity Proxy
This proxy erases user information before connecting to the target website. It’s ideal for users who require maximum privacy, like employees needing to protect their browsing history.
However, some free versions may compromise security.
5. Distorting Proxy
A distorting proxy disguises itself as a regular proxy while masking its true identity. It can make it appear as though you’re browsing from another country.
This is good for hiding location and identity, though some websites may block these proxies.
6. Data Center Proxy
Data center proxies are not tied to an ISP but are provided through a third-party data center.
They offer fast response times and affordability, making them ideal for data collection, but they don’t offer the best anonymity.
7. Residential Proxy
A residential proxy provides an actual, physical device’s IP address, making it more trustworthy than other proxies.
Best for users verifying ads or blocking malicious content, though it tends to be pricier.
8. Public Proxy
Public proxies are free to use and accessible by anyone, offering a basic level of anonymity.
However, they’re often slow and carry a higher risk of data breaches due to shared access.
9. Shared Proxy
Shared proxies are used by multiple users, offering an inexpensive way to surf the web anonymously. While affordable, they come with the risk of being blamed for someone else’s actions, potentially getting you banned from websites.
10. SSL Proxy
An SSL proxy encrypts data between the client and server, making it secure for online transactions.
It’s ideal for businesses wanting to protect sensitive information and improve SEO, but it may result in slower website performance due to encryption.
11. Rotating Proxy
Rotating proxies assign different IP addresses with each connection, allowing for anonymous web scraping.
Great for high-volume tasks, but users should be cautious of services that use public or shared proxies, which could compromise security.
12. Reverse Proxy
A reverse proxy sits in front of web servers and manages incoming requests. It helps distribute traffic and reduce bandwidth load, making it great for popular websites.
However, if compromised, it can expose your server’s architecture and create security risks.
Info: Find out everything you need to know about reverse proxies and how to set them up on our easy-to-use discussion forum!
Advantages of Proxy Server
-
IP Address Concealment
One of the key benefits of using a proxy server is that it hides your IP address. Instead of websites seeing your IP address, they only see the proxy’s IP address, helping protect your privacy while browsing the web.
For example, suppose you use a proxy server in a different country. In that case, websites may think your traffic is coming from there, allowing you to bypass geo-restrictions or browse anonymously. Additionally, hiding your real IP can help prevent cyberattacks, tracking, and unwanted ads targeting your browsing habits.
Request: We recently received a support ticket from a person facing an issue; he said, “Our small business website has been under a DDoS attack for the past two weeks, and it’s been incredibly frustrating. Our web host keeps shutting us down whenever we try to get things back on track. It’s exhausting and feels like we’re fighting an uphill battle.”
Worried About DDoS Attacks?
Our WordPress hosting plans come with cutting-edge security features designed to defend against DDoS attacks, ensuring that your site remains online and fully functional.
-
Bandwidth Savings and Faster Speeds
Proxy servers can improve overall network performance by caching popular websites. When you visit a site like www.example.com, the proxy server checks if it has a recent copy of the site and sends you that saved version. This means that if many people access the site simultaneously through the same proxy server, only one request is made to the website, saving bandwidth and speeding up the browsing experience for everyone.
-
Access Blocked Content
Proxy servers help users bypass content restrictions set by companies or governments. For example, if a local sports game is blocked online, you can connect to a proxy server in a different region, like California, and watch the game as if you were there. This allows you to access content that would otherwise be unavailable in your location. Proxy servers also allow people in countries with strict internet monitoring to access an uncensored internet experience.
Proxy Server Protocols
1. HTTP Proxy
Handles regular web traffic, like browsing the internet. It forwards requests and responses between users and websites, often helping with caching and content filtering.
2. HTTPS Proxy
Specifically manages encrypted HTTPS traffic. It decrypts, checks, and re-encrypts the data before sending it to the backend servers. This proxy ensures security and allows visibility into encrypted traffic while still maintaining end-to-end encryption.
3. SOCKS Proxy
Works at a lower level to handle various types of internet traffic. It connects to destination servers and passes data between users and servers, commonly used for online gaming and file sharing.
4. FTP Proxy
Designed for FTP (File Transfer Protocol) traffic, this proxy manages FTP commands and data transfers between users and servers, offering access control and logging features.
5. SMTP/POP3/IMAP Proxy
Handles email traffic, intercepting and relaying messages between users and email servers. It also provides features like spam filtering and antivirus scanning.
Conclusion
Proxy servers are a valuable business tool, offering enhanced anonymity and security. However, they aren’t a one-size-fits-all solution, and it’s essential to have a clear purpose for using one.
Equally important is choosing a reliable hosting service to protect your data and ensure your website’s stability. A quality hosting provider stores your site on secure servers with advanced protection against cyber threats. If you’re looking for scalable, secure, and flexible solutions, AccuWeb Hosting is here to help. Our hosting plans are designed to handle high traffic, provide ample storage, and support multiple websites, making us a dependable partner for your web hosting needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Are Proxy Servers Secure?
Yes, proxy servers are secure as they act as intermediaries, enhancing the overall security of the system by masking user information and filtering traffic.
2. Can I Set Up My Own Proxy?
Yes, you can set up your own proxy, but it requires server administration skills to configure and maintain it properly.
3. What’s the Difference Between a Proxy Server and a Firewall?
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between the user and the internet, forwarding web requests and responses on behalf of the user. In contrast, a firewall monitors network traffic entering or exiting a system, blocking or allowing data based on security rules to protect against unauthorized access or threats.
(Visited 54 times, 1 visits today)