Proper maintenance is crucial for prolonging the lifespan and for ensuring the efficient operation of your screw air compressor. Here are some essential maintenance tasks specifically tailored for prolonging the lifespan of a screw air compressor.
1. Routine visual inspection: Performing regular visual inspection of your air compressor is an important activity. Check for oil leaks and loose connections. Monitor the compressor’s operating parameters, such as pressure and temperature, to ensure they are within normal ranges. Catching issues early can prevent more significant problems down the line.
2. Lubricating oil: Proper lubrication is essential for minimizing friction and ensuring smooth operation. Check oil levels daily and top it up if necessary, using the recommended oil type. Change the oil at the intervals as recommended by the manufacturer’s guidelines. Never mix oils of different grades as this may lead to varnishing and oil solidification. It is recommended to perform oil analysis at periodic intervals to assess oil quality and determine if an oil change is needed.
3. Air filters: Inspect and clean or replace air filters according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Make use of the clog indicators to check the condition of the air filters. Clogged air filters will reduce the airflow and strain the compressor, leading to decreased efficiency. Punctured air filters will allow dirt/dust into the system thereby damaging the compressor.
4. Oil filters: Oil filters play a critical role in enhancing the life of the compressors. Replace the oil filters at the intervals recommended by the manufacturer’s guidelines to prevents the contaminants from circulating in the system and affecting performance.
5. Air/oil separator: One of the critical part of the screw compressor which removes the oil from the discharge air before it enters the service line. Replace the oil separator element at the intervals recommended by the manufacturer or early if gets choked. Running compressor with choked separator element will increase energy consumed by the compressor.
6. Motor greasing: Electric motors driving the compressors must be re-greased at periodic intervals as recommended by the motor manufacturers. Use the grease as recommended by the manufacturer.
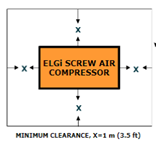
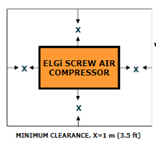
7. Compressor room: Compressor must be installed in a room which is clean, dry, cool and free from dust. There should be sufficient space around the compressor for access during maintenance.

8. Moisture draining: Air compressors produce moisture as they compress air. Drain accumulated moisture from the air/oil separator and receiver tank daily to prevent corrosion and maintain system efficiency. Install auto drain valves in receivers and downstream filters.
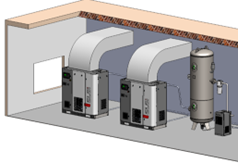
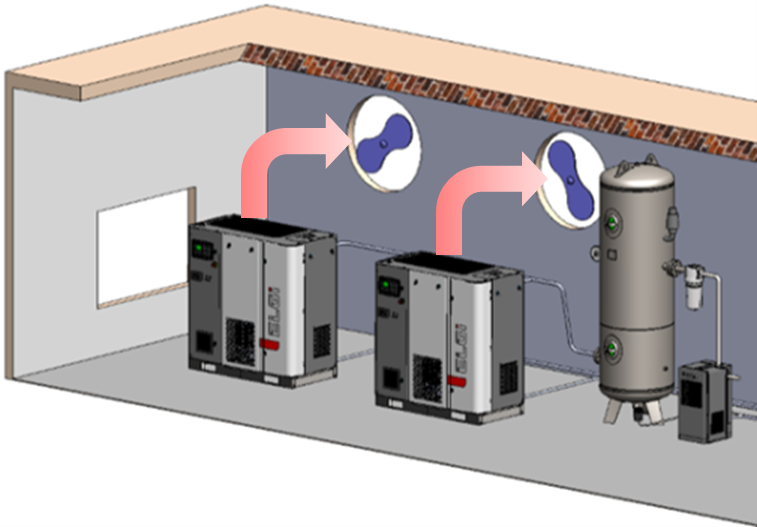
9. Cooling system: Keep the cooling system clean and free from debris. Clean the heat exchangers and the cooling fins at regular intervals to ensure proper heat dissipation, to prevent overheating and to maintain the compressor operating temperature under control. In case of air-cooled compressors, proper ducting is required to be installed at the time of commissioning the compressor to ensure that the hot air from the compressor is exhausted from the compressor room properly.
| Type of ventilation | When | |
|
A |
Natural ventilation |
If room temperature increase |
| B |
Forced ventilation with exhaust fan |
If room temperature increase > 5 Deg C when compared with ambient temperature |
| C |
Forced ventilation with ducting |
If room temperature increase > 5 Deg C when compared with ambient temperature and compressor is in enclosed area |
10. Couplings, belts and pulleys: Check the condition and tension of belts and pulleys to ensure they are properly aligned and functioning without excessive wear. Replace belts and coupling elements if required.
11. Valve maintenance: Control system components of the screw air compressor like intake valve, blowdown valve, minimum pressure valve need maintenance at prescribed intervals which may include cleaning and/or replacing the service kits.
12. Electrical system: Inspect electrical components including contactors, cables, switches and controls for signs of wear or damage. Replace if found necessary.
13. Vibration and noise: Monitor the compressor for unusual vibrations or increased noise levels. Excessive vibration can indicate misalignment or other mechanical issues. Consult the OEM or their authorized distributors if there is any abnormality.
14. Scheduled maintenance: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, which may include more in-depth inspections, servicing, and part replacements at specific intervals.
15. Maintenance log: Maintain a detailed maintenance log, recording all maintenance tasks performed, dates, and any observed issues.
16. Operator training: Train operators on proper usage and maintenance procedures. Educate them about safe practices, proper shutdown procedures, and the importance of regular checks.
17. Major overhauling and OEM services: For major overhauling or servicing and for more complex maintenance tasks or repairs, enlist the services of OEM or their authorized distributors. Regular professional inspections can identify potential issues before they become major problems.
18. Airend: Condition of airend bearings can be monitored using SPM (Shock Pulse Meter) and the overhauling of airend can be planned basis the SPM reports.
Remember, the specific maintenance tasks and intervals can vary based on the compressor’s make and model, as well as the manufacturer’s recommendations. Always refer to the compressor’s O&M manual and follow the guidelines provided in the manual for the best results.