Thermal energy moves from warmer regions to cooler ones through conduction, convection, and radiation. Objects continuously lose heat until they achieve thermal equilibrium, meaning they reach the same temperature as their environment. For instance, a steaming mug of tea will gradually cool until it matches the temperature of the room.
But how that mug looses that heat is what this blog is all about.
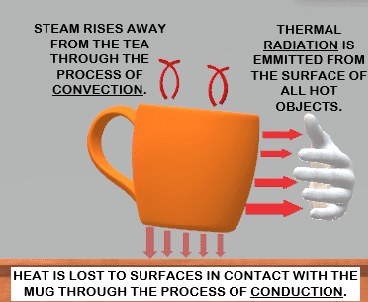
CONDUCTION:
Thermal energy moves through solids mainly via conduction. This phenomenon happens when two solid items with varying temperatures come into contact, enabling heat to transfer from the warmer object to the cooler one. For instance, in the scenario of a hot coffee mug resting on a cold table, the thermal energy shifts from the mug to the table beneath it.
CONVECTION:
Convection refers to the movement of fluids, whether they are liquids or gases, and can occur naturally or be induced by external forces. Fluids can either absorb or release heat, depending on their temperature. Natural convection happens due to variations in density; for instance, steam rises from the top of the mug as the steam rises, colder air is cycled in.
RADIATION:
While the coffee emits infrared radiation as it loses heat, this process is generally less significant compared to conduction and convection in the context of a cup of coffee. This type of heat loss can be felt by holding your hand near a warm coffee cup as shown.
No matter how the heat is transferred to an object, if it needs to be cooled there is a good chance that one of our Application Engineers has approached a similar issue and can help. To discuss, contact us, and we will walk through the best method to eliminate the heat from within your application.
Jordan Shouse
Application Engineer
Send me an Email
Find us on the Web
Like us on Facebook
Twitter: @EXAIR_JS








