Find out what BDLDaemon is on Mac, in what ways it might affect the user experience, and how to prevent its excessive CPU and memory usage
Update:
What is BDLDaemon on your Mac?
The dilemma of whether or not to use third-party antivirus software on Mac has sparked some of the hottest discussions among Apple fans for years. One facet of this long-running polemic comes down to confidence that the operating system’s native security is robust enough to stop malware in its tracks. The other is that present-day threats can easily bypass these defenses. My perspective is somewhere in the middle. Apple undoubtedly does a great job shielding its devices, but antivirus tools can do the heavy lifting to disinfect malware-stricken Macs in scenarios where the users would spend hours or days finding all those rogue Launch Agents and Daemons spawned by bad code.
The rule of thumb, though, is to use a reputable security solution. Bitdefender Antivirus for Mac certainly fits the mold of such software, but its activity has periodically triggered hiccups and problems – no, not in terms of the effectiveness of protection, but in terms of system performance impact. One such example is the heavy CPU and memory load caused by a process named BDLDaemon. Let’s take a closer look at what this entity is on Mac, how it may get out of hand, and what to do about it.
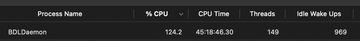
The BDLDaemon CPU and memory overuse may re-infect your Mac multiple times unless you delete all of its fragments, including hidden ones. Therefore, it is recommended to download Combo Cleaner and scan your system for these stubborn files. This way, you may reduce the cleanup time from hours to minutes.
Download Now Learn how Combo Cleaner works. If the utility spots malicious code, you will need to buy a license to get rid of it.
Common BDLDaemon problems and their catalysts on Mac
Most complaints about BDLDaemon misbehavior involve CPU and RAM spikes it causes at times. This, obviously, throws a thick spanner in the works because the Mac becomes noisy as the fan tries to cool down the scorching hardware, and perhaps more obnoxiously, because the machine’s productivity takes a serious hit when the resources are insufficient to handle other tasks. When on battery, energy drain becomes yet another drag. One of the obvious reasons for this overkill is the significant CPU and memory demand during real-time scanning, especially if Bitdefender is configured for thorough, on-access file inspection. This routine can’t possibly take place with low system footprint, and this is normal behavior. But on older Macs or systems with limited resources, it can literally max out processor usage and lead to noticeable slowdowns.
Outdated software or conflicts can be the culprits as well. If macOS or Bitdefender itself isn’t up to date, compatibility issues or bugs can cause BDLDaemon to act up. Conflicts with other security software or system utilities can blow the problem out of proportion. Also, the program’s scanning cache or configuration files might become corrupted over time, only to make the daemon work harder than necessary. This condition can manifest itself through RAM swamping or persistently high CPU usage even when no scan is underway.
First fixes on the checklist
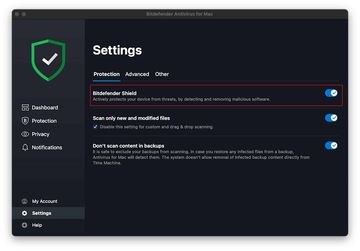
As often happens, troubleshooting is a matter of trial and error. Assuming that the adverse situation likely stems from bugs at the software level, a good starting point is to check for and install macOS updates or a newer version of the anti-malware tool if available. Another potentially effective workaround is to temporarily turn off the Bitdefender Shield module, which can be found under the “Protection” tab in the app’s preferences (see screenshot below). This will stop real-time scanning, limiting BDLDaemon to manual scans only. If this helps, consider tweaking scan settings to exclude non-critical folders, such as large media libraries, via Antivirus > Exceptions. Also, if you’ve opted for scheduled scans, set those to run during off-peak hours.
Speaking of the fixes, the train of thought could well move into the area of malware activity. When dealing with stubborn threats such as rootkits, spyware, or Mac ransomware, the BDLDaemon routine can intensify to an extent where it dramatically cranks up its CPU and memory consumption. This can enter a loop condition that doesn’t stop after a virus scan or disinfection attempt. Furthermore, some strains of malware can mimic legitimate daemons or inject rogue components into them to avoid detection, which is often accompanied by inconsistencies at the system level and performance issues. This is an unlikely scenario, to be honest, but it’s worth putting it to the test. To err on the side of caution, follow the steps below and check your Mac for threats that might be flying under the radar of your current security app.
BDLDaemon high CPU virus manual removal from Mac
The steps listed below will walk you through the removal of this malicious application. Be sure to follow the instructions in the specified order.
-
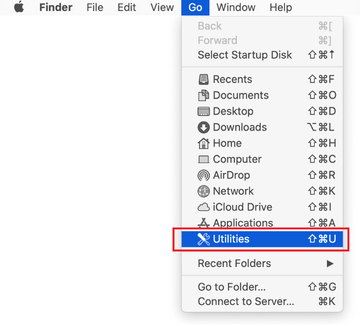
Expand the Go menu in your Mac’s Finder bar and select Utilities as shown below.
-
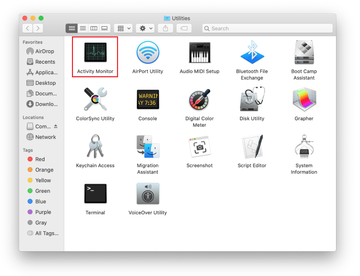
Locate the Activity Monitor icon on the Utilities screen and double-click on it.
-
In the Activity Monitor app, look for a process that appears suspicious. To narrow down your search, focus on unfamiliar resource-intensive entries on the list. Keep in mind that its name isn’t necessarily related to the way the threat is manifesting itself, so you’ll need to trust your own judgement. If you pinpoint the culprit, select it and click on the Stop icon in the upper left-hand corner of the screen.
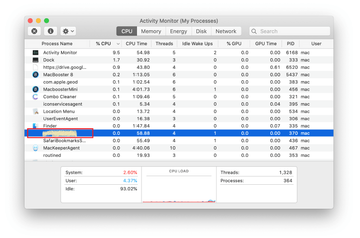
-
When a follow-up dialog pops up asking if you are sure you want to quit the troublemaking process, select the Force Quit option.
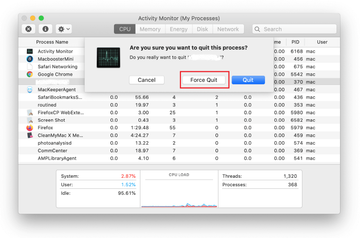
-
Click on the Go menu icon in the Finder again and select Go to Folder. You can as well use the Command-Shift-G keyboard shortcut.
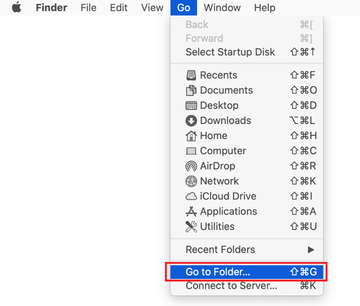
-
Type /Library/LaunchAgents in the folder search dialog and click on the Go button.
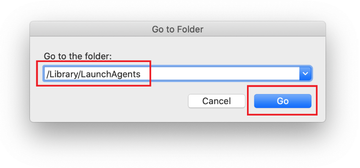
-
Examine the contents of the LaunchAgents folder for dubious-looking items. Be advised that the names of files spawned by malware may give no clear clues that they are malicious, so you should look for recently added entities that appear to deviate from the norm.
As an illustration, here are several examples of LaunchAgents related to mainstream Mac infections: com.updater.mcy.plist, com.avickUpd.plist, and com.msp.agent.plist. If you spot files that don’t belong on the list, go ahead and drag them to the Trash.
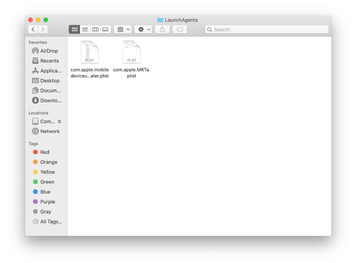
-
Use the Go to Folder lookup feature again to navigate to the folder named ~/Library/Application Support (note the tilde symbol prepended to the path).
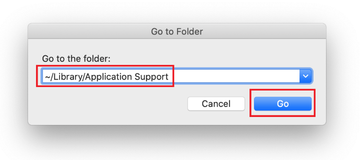
-
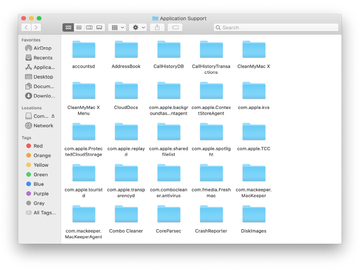
When the Application Support directory is opened, identify recently generated suspicious folders in it and send them to the Trash. A quick tip is to look for items whose names have nothing to do with Apple products or apps you knowingly installed. A few examples of known-malicious folder names are ProgressSite and IdeaShared.
- Enter ~/Library/LaunchAgents string (don’t forget to include the tilde character) in the Go to Folder search area.
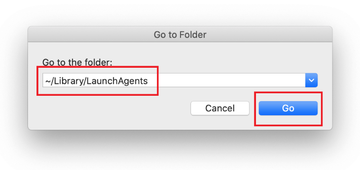
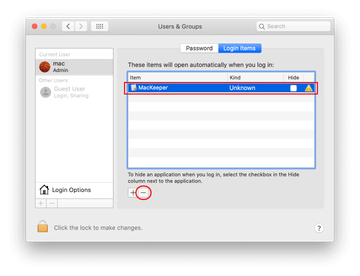
- The system will display LaunchAgents residing in the current user’s Home directory. Look for dodgy items related to rogue BDLDaemon process (see logic highlighted in subsections above) and drag the suspects to the Trash.
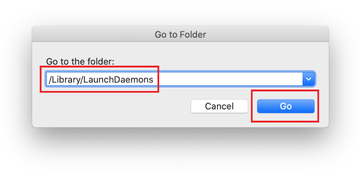
- Type /Library/LaunchDaemons in the Go to Folder search field.
- In the LaunchDaemons path, try to pinpoint the files the malware is using for persistence. Several examples of such items cropped by Mac infections are com.apple.sysmond.plist, com.startup.plist, and com.ExpertModuleSearchDaemon.plist. Delete the sketchy files immediately.
- Click on the Go menu icon in your Mac’s Finder and select Applications on the list.
- Find the entry for an app that clearly doesn’t belong there and move it to the Trash. If this action requires your admin password for confirmation, go ahead and enter it.

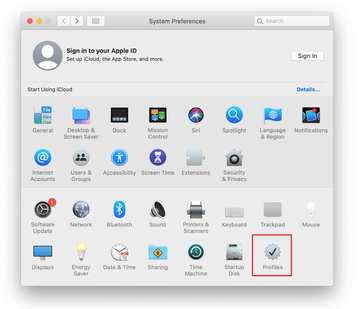
- Expand the Apple menu and select System Preferences.
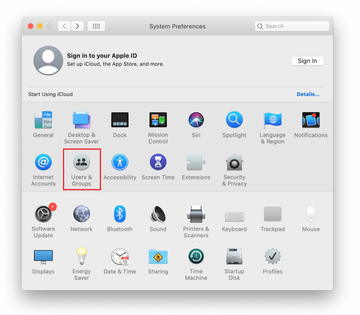
- Proceed to Users & Groups and click on the Login Items tab.
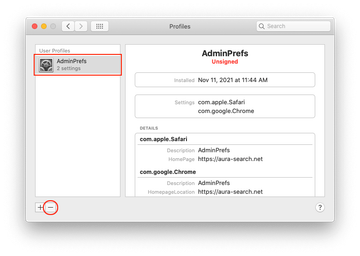
- Now select Profiles under System Preferences. Look for a malicious item in the left-hand sidebar. Several examples of configuration profiles created by Mac adware include TechSignalSearch, MainSearchPlatform, AdminPrefs, and Safari Settings. Select the offending entity and click on the minus sign at the bottom to eliminate it.
Get rid of BDLDaemon virus in web browser on Mac
To begin with, the web browser settings taken over by the BDLDaemon virus should be restored to their default values. Although this will clear most of your customizations, web surfing history, and all temporary data stored by websites, the malicious interference should be terminated likewise. The overview of the steps for completing this procedure is as follows:
- Remove BDLDaemon virus from Safari
-
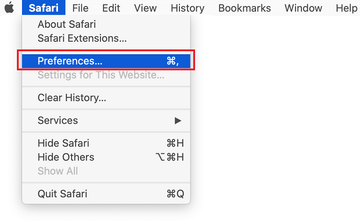
Open the browser and go to Safari menu. Select Preferences in the drop-down list.
-
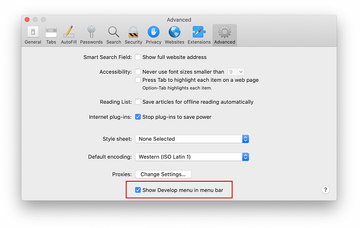
Once the Preferences screen appears, click on the Advanced tab and enable the option saying “Show Develop menu in menu bar”.
-
Now that the Develop entry has been added to the Safari menu, expand it and click on Empty Caches.
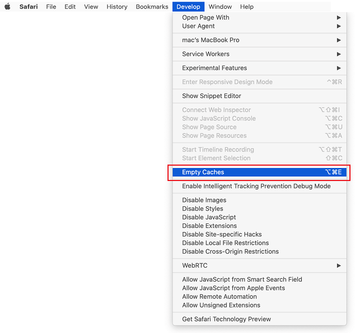
-
Now select History in the Safari menu and click on Clear History in the drop-down list.
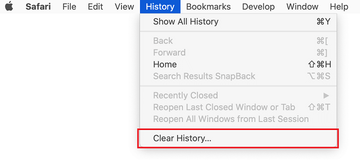
-
Safari will display a dialog asking you to specify the period of time this action will apply to. Select all history to ensure a maximum effect. Click on the Clear History button to confirm and exit.
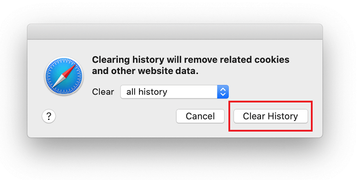
-
Go back to the Safari Preferences and hit the Privacy tab at the top. Find the option that says Manage Website Data and click on it.
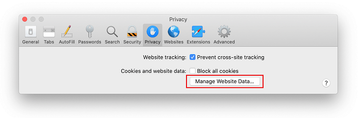
-
The browser will display a follow-up screen listing the websites that have stored data about your Internet activities. This dialog additionally includes a brief description of what the removal does: you may be logged out of some services and encounter other changes of website behavior after the procedure. If you’re okay with that, go ahead and click on the Remove All button.
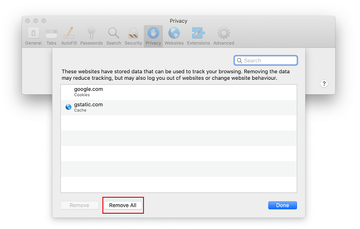
-
Restart Safari
-
- Remove BDLDaemon in Google Chrome
-
Open Chrome, click the Customize and control Google Chrome (⁝) icon in the top right-hand part of the window, and select Settings in the drop-down
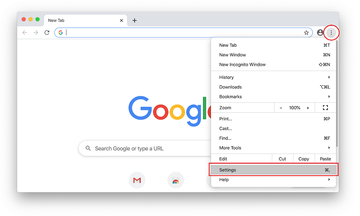
-
When on the Settings pane, select Advanced
-
Scroll down to the Reset settings section.
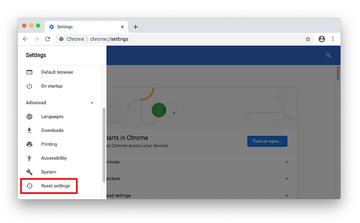
-
Confirm the Chrome reset on a dialog that will pop up. When the procedure is completed, relaunch the browser and check it for malware activity.
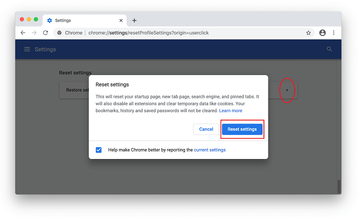
-
- Remove BDLDaemon from Mozilla Firefox
-
Open Firefox and go to Help – Troubleshooting Information (or type about:support in the URL bar and press Enter).
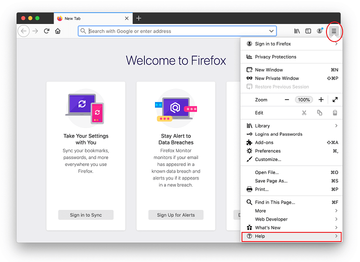
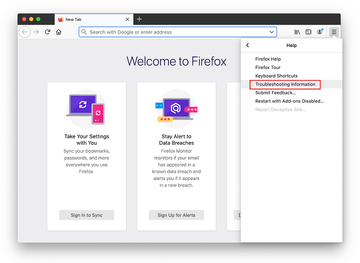
-
When on the Troubleshooting Information screen, click on the Refresh Firefox button.
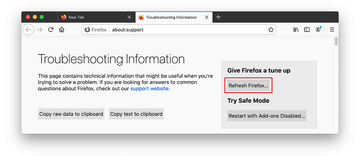
-
Confirm the intended changes and restart Firefox.
-
Fix BDLDaemon CPU and memory overuse on Mac using Combo Cleaner removal tool
The Mac maintenance and security app called Combo Cleaner is a one-stop tool to detect and remove BDLDaemon virus. This technique has substantial benefits over manual cleanup, because the utility gets hourly virus definition updates and can accurately spot even the newest Mac infections.
Furthermore, the automatic solution will find the core files of the malware deep down the system structure, which might otherwise be a challenge to locate. Here’s a walkthrough to sort out the BDLDaemon issue using Combo Cleaner:
-
Download Combo Cleaner installer. When done, double-click the combocleaner.dmg file and follow the prompts to install the tool onto your Mac.
By downloading any applications recommended on this website you agree to our Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy. The free scanner checks whether your Mac is infected. To get rid of malware, you need to purchase the Premium version of Combo Cleaner.
-
Open the app from your Launchpad and let it run an update of the malware signature database to make sure it can identify the latest threats.
-
Click the Start Combo Scan button to check your Mac for malicious activity as well as performance issues.
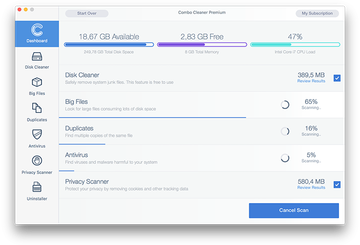
-
Examine the scan results. If the report says “No Threats”, then you are on the right track with the manual cleaning and can safely proceed to tidy up the web browser that may continue to act up due to the after-effects of the malware attack (see instructions above).
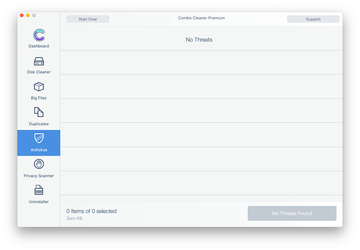
-
In case Combo Cleaner has detected malicious code, click the Remove Selected Items button and have the utility remove BDLDaemon threat along with any other viruses, PUPs (potentially unwanted programs), or junk files that don’t belong on your Mac.
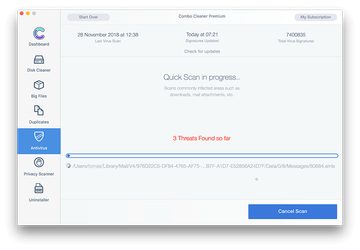
-
Once you have made doubly sure that the malicious app is uninstalled, the browser-level troubleshooting might still be on your to-do list. If your preferred browser is affected, resort to the previous section of this tutorial to revert to hassle-free web surfing.








