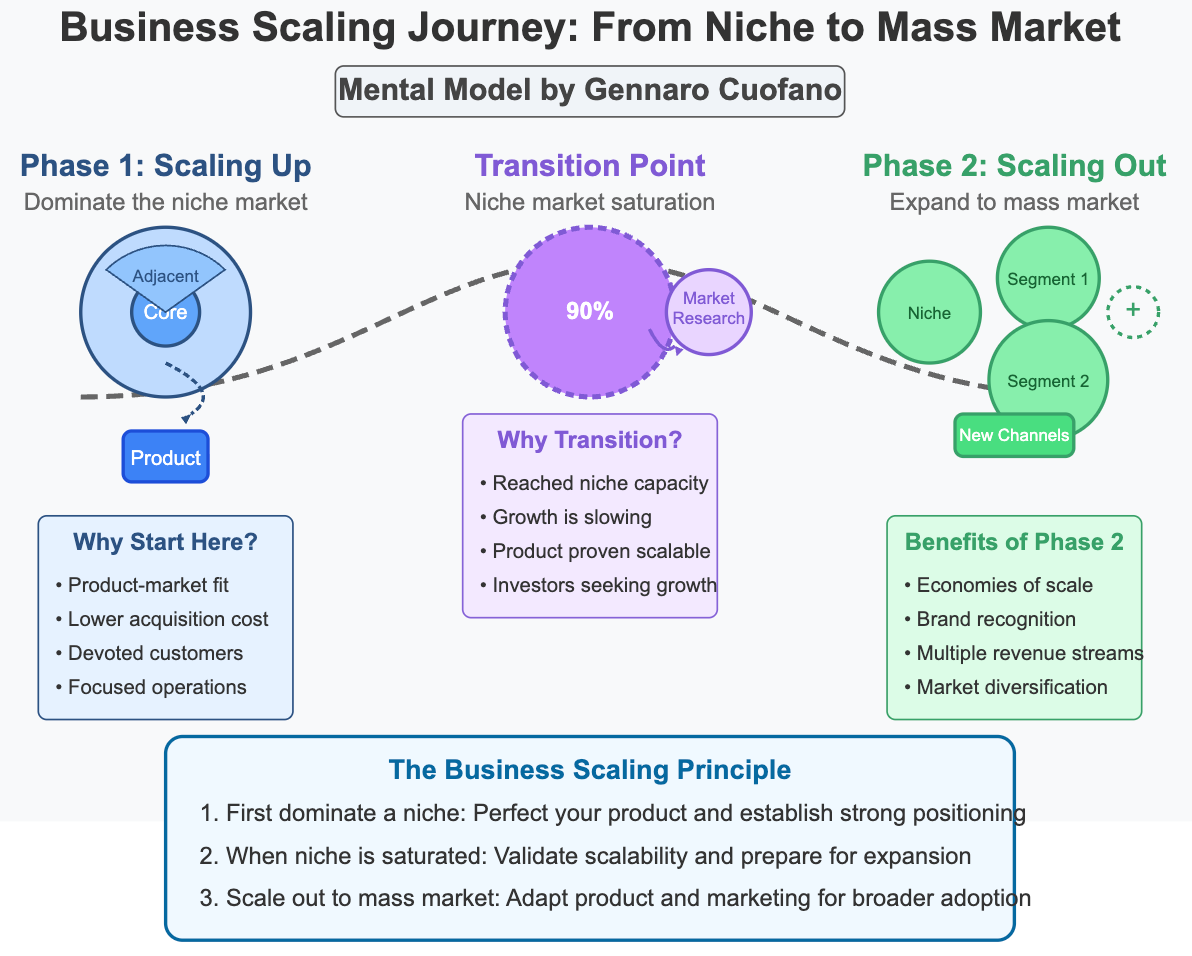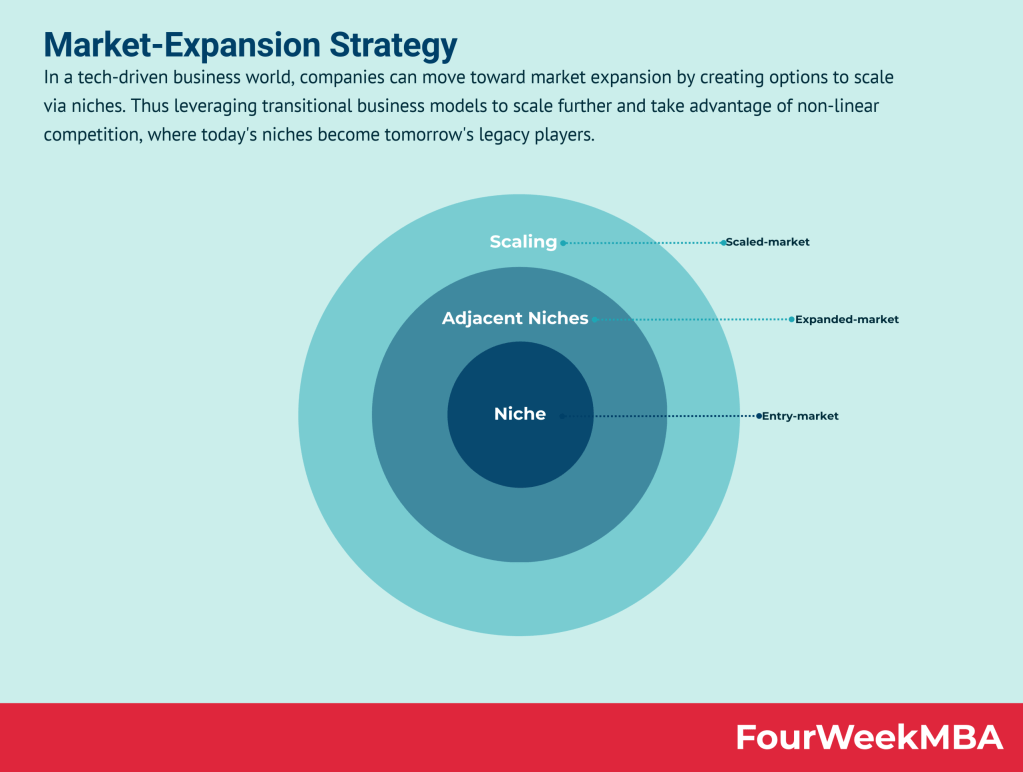
Today’s niche is tomorrow’s mass market.
In business scaling, I’ve explained how companies can move toward market expansion in a tech-driven business world by creating niche-based scaling options.
Thus, transitional business models can be leveraged to scale further and take advantage of non-linear competition, where today’s niches become tomorrow’s legacy players.
Let me show you the essence of a market expansion strategy!
Let me show you a few key concepts to visualize and then a process to get there…
Help customers seamlessly integrate your tools and services on HubSpot
Thousands of organizations trust HubSpot to connect their essential software, and now you can deliver solutions that drive more value by surfacing functionality exactly where users need it. UI extensions are the first step toward a more open dev platform and a new way to build apps on HubSpot.
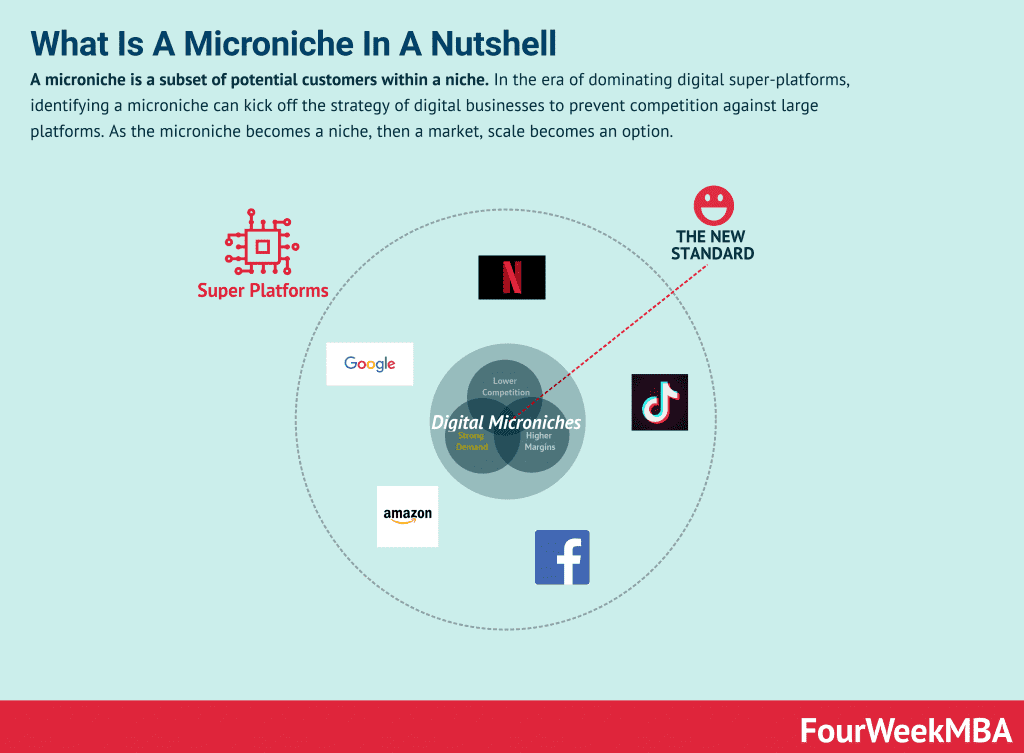
Start by identifying a specific subset of a broader niche or market. This subset should be specific enough to target precisely but have enough potential customers to make it viable.
-
Purpose: Avoiding direct competition with larger, established players.
-
Example: Instead of targeting the broad category of “fitness enthusiasts,” focus on “vegan fitness enthusiasts who practice yoga.”
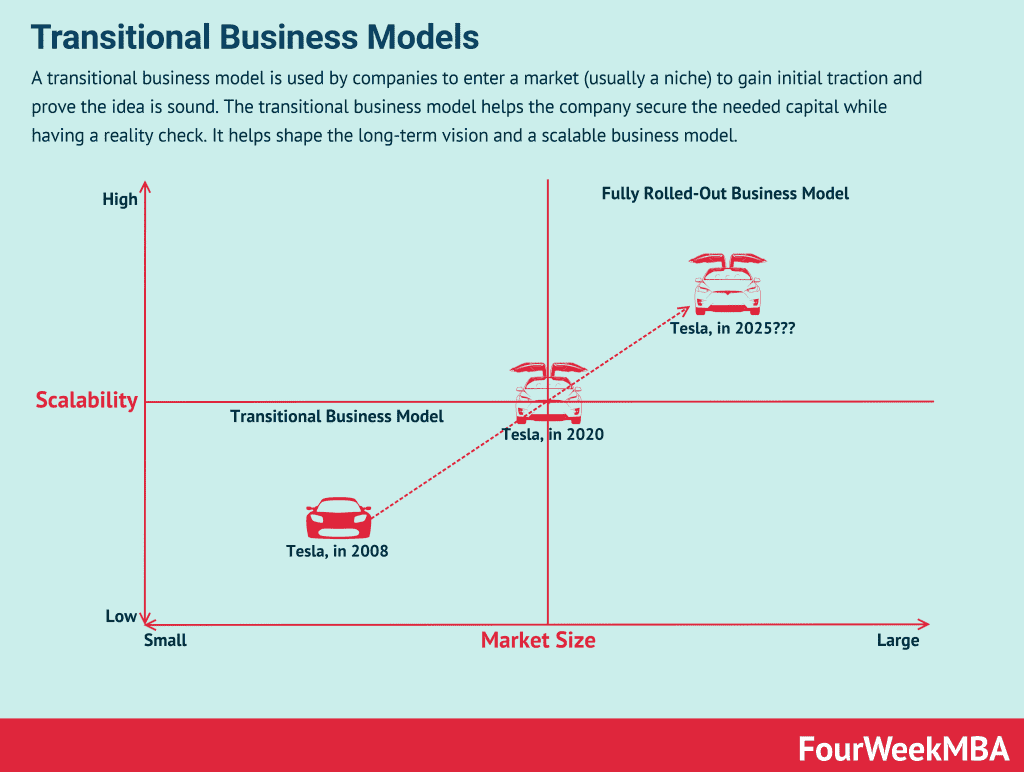
Once you’ve identified your microniche, use a transitional business model to enter the market and gain initial traction.
-
Purpose: To validate the business idea, secure initial capital, and refine the long-term vision.
-
Example: Start by offering a subscription-based service to this niche, then transition to a freemium model as you gain traction.
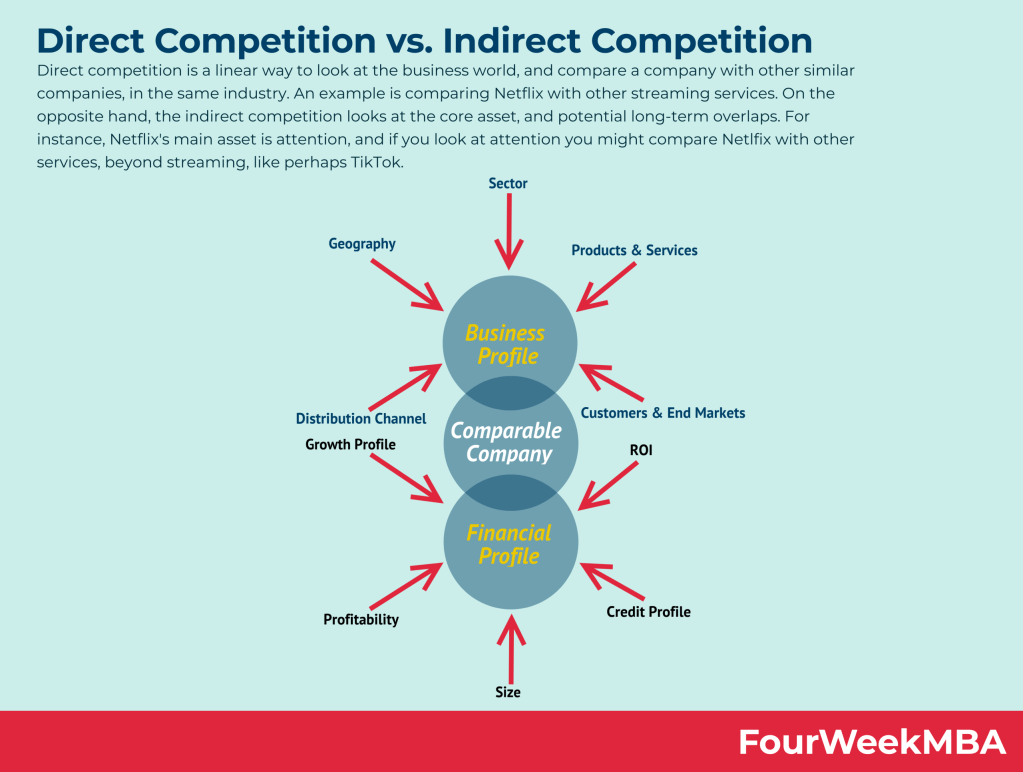
Look beyond direct competitors in your industry and consider indirect competitors who might be targeting the same core assets or attention of your audience.
-
Purpose: To identify potential threats and opportunities outside the direct line of competition.
-
Example: If you’re a streaming service, don’t just compare yourself to other streaming platforms. Consider platforms like TikTok that capture audience attention in different ways.
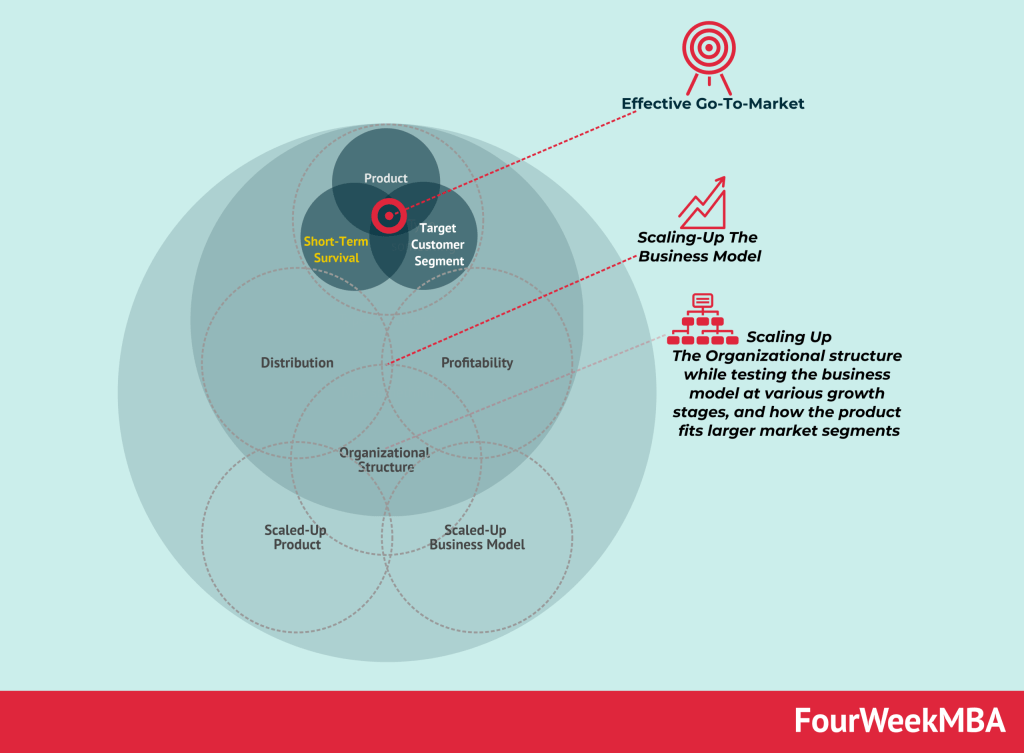
After validating the product or service within the microniche, begin scaling the business to target wider market segments.
Example: Beyond Meat. Instead of targeting the broad category of “vegetarians,” Beyond Meat specifically targeted the microniche of “meat-lovers looking for plant-based alternatives that taste like meat.” Their products are designed to mimic the taste and texture of meat, appealing to both vegetarians and meat-eaters wanting to reduce meat consumption.
Example: Airbnb. Initially, Airbnb targeted the microniche of people attending conferences who needed a place to stay. They started by renting out air mattresses in their apartment (hence the name “Air Bed & Breakfast”). As they validated this model and secured initial capital, they transitioned into a full-fledged platform for people to rent out their homes or rooms to travelers.
Example: Netflix. Initially, Netflix might have viewed its primary competition as other DVD rental services. However, as they transitioned to streaming, their competition became more varied, from other streaming platforms like Hulu to cable TV to video-sharing platforms like YouTube, and even video game platforms. They’re all vying for the same thing: viewers’ attention.
Example: Spotify. Spotify began in Sweden, targeting the microniche of Swedish music lovers looking for a legal way to stream music. Once they gained traction and validated their subscription-based model, they expanded to other European countries before entering the U.S. market. They then diversified their offerings with podcast hosting and streaming.
-
Niche Positioning and Microniche Identification: In the era of dominant digital super-platforms, identifying a microniche, which is a subset of potential customers within a niche, can be a strategic approach for digital businesses. Starting with a microniche helps prevent direct competition against large platforms, and as it grows into a niche and eventually a market, scaling becomes a viable option.
-
Transitional Business Model for Traction and Capital: Transitional business models are used by companies entering a market, often a niche, to gain initial traction and validate their ideas. It serves as a reality check and allows the company to secure the necessary capital. This phase helps shape the long-term vision and establish a scalable business model.
-
Non-Linear Competition: Rather than engaging in direct competition with similar companies in the same industry, non-linear competition focuses on core assets and potential long-term overlaps. For example, a company like Netflix might be compared not only with other streaming services but also with platforms in different domains, like TikTok, as both compete for attention.
-
Business Scaling and Market Segments: Business scaling involves the transformation of a business as its product is validated by wider market segments. It starts by gaining traction in a small market segment and then aligning the product, business model, and organizational design to enable expansion to broader market segments.
Real World Case Studies
Zoom
-
Microniche Strategy: Zoom initially targeted businesses and professionals looking for a reliable video conferencing solution.
-
Transitional Business Model: They offered a freemium model to gain traction in the business communication niche.
-
Non-Linear Competition: Zoom competes with traditional video conferencing providers but also with messaging platforms integrating video calls.
-
Business Scaling: Zoom expanded its services for virtual events, webinars, and remote work, becoming a household name during the COVID-19 pandemic.
-
Microniche Strategy: LinkedIn began as a platform for professionals to network and find job opportunities.
-
Transitional Business Model: They offered premium subscriptions for job seekers and recruiters to validate their revenue model.
-
Non-Linear Competition: LinkedIn competes with other job search platforms but also with social media platforms and professional associations.
-
Business Scaling: LinkedIn expanded into content sharing, skill endorsements, and B2B marketing solutions.
Slack
-
Microniche Strategy: Slack started as an internal communication tool for tech startups and small teams.
-
Transitional Business Model: They offered a freemium model, gaining popularity among small businesses.
-
Non-Linear Competition: Slack competes with traditional email communication but also with project management and collaboration tools.
-
Business Scaling: Slack expanded its offerings to serve larger enterprises and integrate with various business apps.
Stripe
-
Microniche Strategy: Stripe initially focused on providing payment processing solutions for online startups and developers.
-
Transitional Business Model: They offered a developer-friendly API, validating their model among early adopters.
-
Non-Linear Competition: Stripe competes with traditional payment processors but also with fintech companies offering payment solutions.
-
Business Scaling: Stripe expanded its services to cater to larger enterprises and international markets.
Dropbox Business
-
Microniche Strategy: Dropbox started as a file-sharing solution for individual users and small teams.
-
Transitional Business Model: They offered team collaboration features to validate their enterprise model.
-
Non-Linear Competition: Dropbox Business competes with other cloud storage providers but also with document management and productivity platforms.
-
Business Scaling: Dropbox Business expanded its offerings with advanced security and administrative controls for larger organizations.
Etsy
-
Microniche Strategy: Etsy began as a marketplace for handmade and vintage goods, targeting artisans and craft enthusiasts.
-
Transitional Business Model: They validated their concept among sellers and buyers passionate about unique and handcrafted items.
-
Non-Linear Competition: Etsy competes with other e-commerce platforms but also with local craft fairs and art markets.
-
Business Scaling: Etsy expanded its product categories and introduced features to help sellers grow their businesses.
DoorDash
-
Microniche Strategy: DoorDash started by offering food delivery services to urban customers looking for restaurant delivery.
-
Transitional Business Model: They validated their model by partnering with local restaurants and gaining customer loyalty.
-
Non-Linear Competition: DoorDash competes with other food delivery platforms but also with grocery delivery services.
-
Business Scaling: DoorDash expanded its services to include grocery and convenience store delivery, becoming a leading food delivery platform.
Twitch
-
Microniche Strategy: Twitch began as a live streaming platform for gamers and gaming enthusiasts.
-
Transitional Business Model: They offered a way for gamers to monetize their streams through ads and subscriptions, validating the concept.
-
Non-Linear Competition: Twitch competes with other live streaming platforms but also with social media platforms offering live video features.
-
Business Scaling: Twitch expanded to include live streaming content beyond gaming, such as music, art, and talk shows.
Peloton
-
Microniche Strategy: Peloton targeted fitness enthusiasts seeking interactive and high-quality home workouts.
-
Transitional Business Model: They offered subscription-based live and on-demand fitness classes, validating their concept.
-
Non-Linear Competition: Peloton competes with traditional gym memberships but also with other home fitness equipment providers.
-
Business Scaling: Peloton expanded its product line to include additional exercise equipment and diversified its content offerings.
Robinhood
-
Microniche Strategy: Robinhood initially focused on providing commission-free stock trading for millennials and novice investors.
-
Transitional Business Model: They offered a user-friendly mobile app, attracting early adopters and validating their approach.
-
Non-Linear Competition: Robinhood competes with traditional brokerage firms but also with fintech companies offering investment apps.
-
Business Scaling: Robinhood expanded its services to include cryptocurrency trading and introduced advanced investment tools.
Read Also:
Ciao!
With ♥️ Gennaro, The Business Engineer