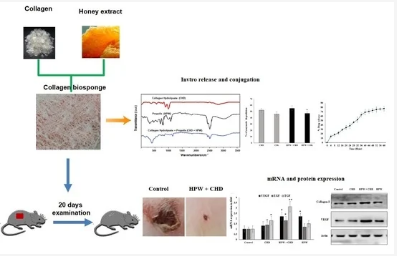
In this study, collagen hydrolysates (CHDs) were fabricated with honey-propolis wax (HPW), structurally modified as a sponge matrix, and experimentalized on wound healing in a mouse model. The scaffold was characterized by means of in vitro enzymatic degradation; in vitro HPW release; and in vivo wound-healing mouse model, wound-healing-specific RNA, transcripts, and protein markers. The functional activity of the HPW extracted from raw propolis was determined using total flavonoids, antioxidant scavenging assays, and anti-hemolytic principles.
These interesting results were further confirmed using mRNA and protein growth factors from the wound, which enhanced the load of collagen-I in the wound site. In conclusion, CHDs-HPW exhibited a significant reduction in inflammation and inflammatory markers and helped to obtain a faster wound-healing process in a mouse model. The newly engineered biosponge could be developed as a promising therapeutic approach for the regeneration and repair of damaged human skin in the future.