
Artificial Intelligence is transforming industries and creating new career opportunities for people from all backgrounds. You don’t need a Ph.D. in computer science, as the domain requires not just engineers but also professionals in domain knowledge. PwC estimates AI will contribute over $15 trillion to the global economy by 2030, driving strong demand for AI talent. This article will provide you with comprehensive steps for professionals from technical and non-technical roles to transition into an AI career.
Why transition to AI?
Before prepping for the transition, let’s learn Why? AI is so much in trend nowadays. It’s not just a vogue or a trend that disrupts the market. It’s a mainstay in the industry and would continue to affect the market as it has done till now. Workflows are getting streamlined by the day, and more and more jobs that previously required human intervention are getting automated. The talent scarcity based on the latest job survey is apparent, and AI is further exacerbating it. Therefore, it makes sense why people are augmenting their skills using artificial intelligence to become more industry-ready.
With the Why? taken care of, let’s learn How? can we make that happen?
How to Transition: A Step-by-Step Plan
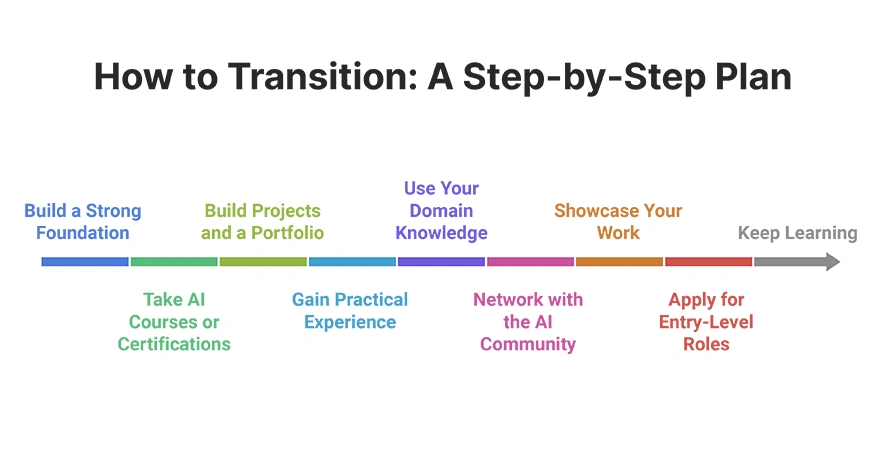
Entering the AI field is a journey that you can tackle step by step. The following is a roadmap to guide your transition, whether you’re coming from a related technical field or starting fresh from a different industry. This plan incorporates tips on education, practical experience, and networking:
1. Build a Strong Foundation
Start by learning basic programming via a beginner-friendly language such as Python. Brush up on math, especially statistics and linear algebra. Develop data literacy through tools like Excel, SQL, and Pandas. These are the essential skills you’ll need daily in AI work, so ensure you’re comfortable working with data and writing simple code. The following list outlines the essential competencies and specialized knowledge for major AI subfields:
- Programming Languages: Proficiency in programming is fundamental. Python is a good starting choice as a programming language in AI due to its simplicity and vast ecosystem of AI libraries.
- Machine Learning: A comprehensive understanding of machine learning (ML) algorithms and deep learning is crucial. ML involves algorithms that enable computers to “learn from data and make predictions,” including supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning.
- Data Handling and Analysis: AI professionals must be adept at data. This includes data management, preprocessing, and wrangling large datasets. Skills in SQL and working with databases or big data tools (like Hadoop/Spark) are valuable for handling big data.
2. Take AI Courses or Certifications
Enroll in beginner-friendly AI or ML courses online. Once comfortable, progress to specialized areas like deep learning or NLP. Certifications help prove your knowledge, but focus on applying what you learn. Avoid staying stuck in endless tutorials, and balance theory with practice.
3. Build Projects and a Portfolio
Apply your skills by working on small, real-world projects. Use datasets from platforms like Kaggle. Build models, analyze results, and share your code on GitHub. A strong portfolio shows that you can solve problems and are on your way to becoming a data professional.
4. Gain Practical Experience
Seek internships, freelance projects, or open-source contributions. Volunteer for data-driven initiatives to gain real-world exposure. These experiences help you learn teamwork, version control, and industry tools—skills that go beyond classroom learning.
5. Use Your Domain Knowledge
Combine your experience with AI. For example, use ML in finance, marketing, or healthcare if that’s your background. This makes your profile unique and valuable to employers looking for industry-aware AI talent.
Join AI communities online and offline. Participate in Kaggle, Reddit, LinkedIn, or local meetups. Networking helps you learn from others, find mentors, and discover job opportunities through referrals or collaborations.
7. Showcase Your Work
Update your resume with your AI skills and projects. Maintain a clean GitHub profile and consider putting yourself out there via SNS (Social Networking Site). Employers appreciate clear communication and well-documented work that showcases real impact.
8. Apply for Entry-Level Roles
Look for junior roles like data analyst, ML intern, or AI associate. Tailor your resume for each role and be ready to explain your projects in interviews. Sometimes, starting in a related role can lead you to AI internally.
9. Keep Learning
AI evolves quickly. Follow newsletters, blogs, or research summaries to stay updated. Learn new tools, try recent models, and deepen your focus as you grow. Staying curious and adaptable is key to long-term success in AI.
The aforementioned steps would assist you in penetrating the elusive AI industry. It’s a lot of work, but thousands of people have successfully made this transition, and with dedication and persistence, you can too.
With How? taken care of, we’ll move over to What? are the pathways to AI.
Common Career Pathways into AI
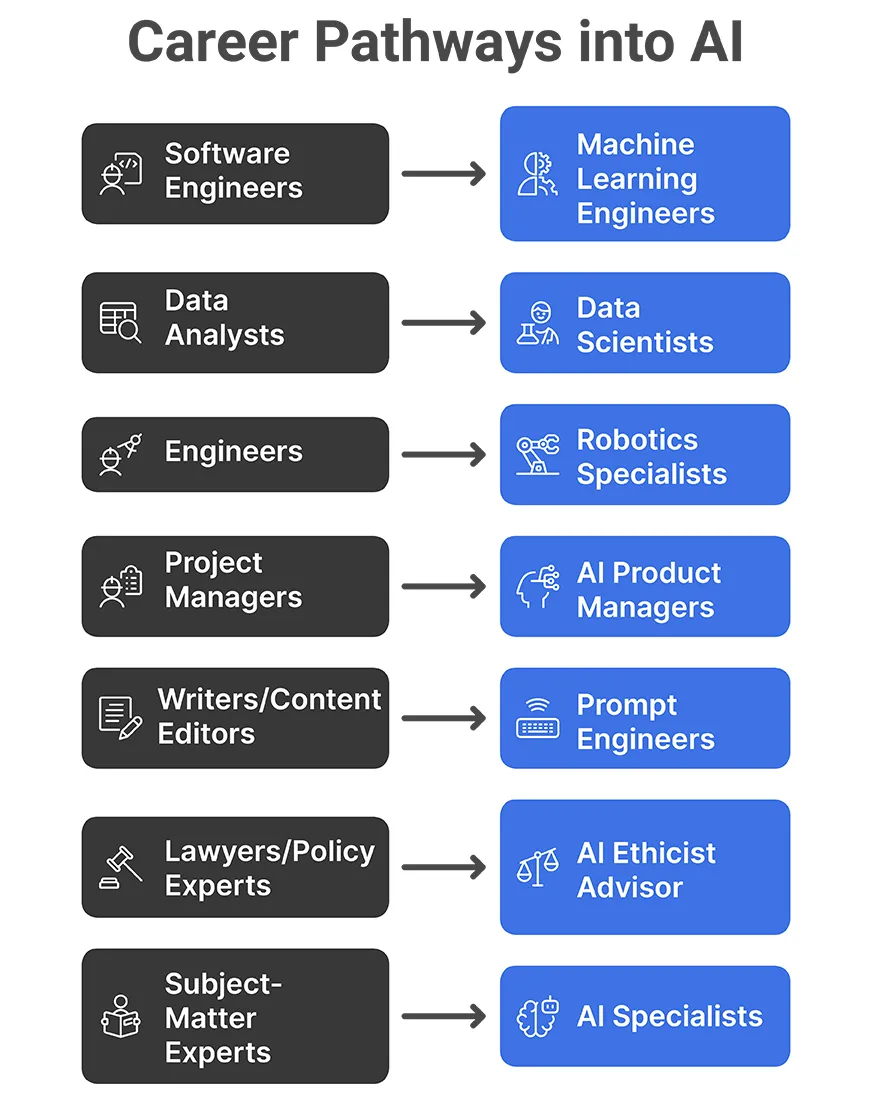
Technical Backgrounds
If you have a technical background, you already possess transferable skills for AI. For example:
- Software Engineers → Machine Learning Engineers: A Strong programming background makes software developers a natural candidate to build AI models and pipelines. Many pivot by learning machine learning algorithms and data science techniques to transition into ML Engineer or Data Scientist roles.
- Data Analysts → Data Scientists: Experience with data manipulation, visualization, and analytics provides a foundation for training AI/ML models. Business Intelligence analysts skilled in data analysis and visualization can leverage those skills for “data-driven decision-making” in data science.
- Engineers (Mechanical, Electrical) → Robotics Specialists: Engineers with math and systems knowledge can learn AI to work on robotics and autonomous systems. For instance, a mechanical engineer could upskill in computer vision to build smart robots.
Non-Technical Backgrounds
AI needs professionals from diverse fields. Non-coders can break into AI through roles that emphasize domain expertise and soft skills:
- Project Managers → AI Product Managers: Project managers and product owners can transition to AI Product Management, where they bridge tech and customer needs. These roles require “business acumen, communication, project management, user research, and a basic understanding of AI” rather than deep coding.
- Writers/Content Editors → Prompt Engineers: Professionals in content, editing, or UX writing are now becoming prompt engineers, crafting effective prompts for AI models. This role is “part writing, part user experience, part creative logic puzzle,” requiring strong language and logic skills, but “you don’t need to code”. Practicing with tools like ChatGPT and building a portfolio of AI-generated content can showcase these skills.
- Lawyers, or Policy Experts → AI Ethicist/Policy Advisor: Those with backgrounds in ethics, law, or public policy can become AI Ethicists or AI Policy Advisors. These professionals ensure AI systems are fair, transparent, and legally compliant. They focus on governance and policy rather than programming, and help AI companies gravitate towards responsible AI.
- Subject-Matter Experts → AI Specialists: Domain experts (in health, finance, education, etc.) can leverage their expertise to develop AI solutions for their field. For example, a doctor or biologist might become an AI specialist in healthcare, working with data scientists to build medical AI tools. Their domain knowledge is invaluable for ensuring AI addresses real-world problems. In fact, “professionals from diverse fields often bring unique perspectives that lead to innovative AI solutions”.
Key Takeaway
Your transferable skills can define or re-fine your AI pathway. The AI industry welcomes people who understand its capabilities and limitations in different contexts. Thanks to democratization through no-code tools, prompt engineering, and the need for interdisciplinary insight, the domain has become a welcoming one for those lacking a predisposition to technology.
Here are some of the people who have successfully made the transition to AI:
- Zahiruddin Tavargere, previously a Senior Principal Software Engineer at Dell, transitioned into an AI Engineer role in November 2023. Now, he leads a Generative AI team, utilizing data engineering, ML models, and MLOps to address business challenges.
- Gabriel Petersson, a self-taught AI researcher, transitioned from product engineering to AI research. Now, he’s a Research Scientist at OpenAI, working on realistic video generation as part of the Sora team.
Typical AI Job Roles, Responsibilities, and Salary Expectations
AI and related fields encompass a variety of job titles. Here we outline some common roles, what they do, and typical salary ranges. Note that salaries vary by country and experience, but AI roles generally pay well above the average for all jobs due to the high demand for these skills.
| Role | Typical Responsibilities | Avg Salary (INR/year) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Scientist | Clean, analyze data; build ML models; derive business insights. Blend of stats, coding, and communication. | ₹10–20 LPA (Entry: ₹7–10L; Senior: ₹20–35L+) |
| Machine Learning Engineer | Develop and deploy ML models in production; optimize for performance. Strong coding + ML skills. | ₹12–25 LPA (Entry: ₹9–12L; Senior: ₹25–40L+) |
| AI Research Scientist | Research new AI methods (often in NLP/CV); publish papers; prototype algorithms. Usually PhD-qualified. | ₹10–22 LPA (Entry: ₹8–12L; Industry senior: ₹30–50L+) |
| NLP Engineer | Build systems that understand or generate human language (chatbots, text mining, LLMs). | ₹12–25 LPA (Experienced: ₹30–40L+) |
| Computer Vision Engineer | Build AI systems for image/video data (e.g., facial recognition, medical imaging). | ₹11–22 LPA (Experienced: ₹30–40L+) |
| AI Engineer / AI Specialist | Generalist or specialized AI expert applying diverse techniques (NLP, CV, etc.) across projects. | ₹15–30 LPA (Senior/Specialist: ₹35–50L+) |
| Data Analyst | Analyze trends, build dashboards, and support decision-making. Often, the entry point into data/AI careers. | ₹5–10 LPA (Experienced: ₹12–15L+) |
Degrees and Certifications for AI
Formal Degrees
A Master’s in AI, Data Science, or Machine Learning is often required and preferred for AI roles, especially for data scientist positions. PhDs are typically needed for research or specialized roles. A Master’s or even a Bachelor’s degree with skills can suffice for entry-level or associate positions.
That said, formal education isn’t the only path. Many online courses and certifications can help you gain credentials and skills:
- Foundational AI Courses: Andrew Ng’s “AI For Everyone” is a good starting point for newcomers, providing a non-technical overview of AI. His Machine Learning course on Coursera is great for those wanting to learn machine learning.
- Specialized Online Programs: Programs like Coursera’s Deep Learning Specialization are excellent for building deep AI expertise and hands-on skills like Python and ML.
- University Certificates (Online): Universities like Stanford and MIT offer online AI-related graduate certificates. These are intensive and often require a math/programming background, but they can strengthen your resume. Stanford University Graduate Certificates (Online) and MIT AI Graduate Certificates (Online) are great options.
- MOOCs and Micro-credentials: Platforms like edX, Udacity, and DataCamp offer courses like Udacity’s AI Nanodegree and edX’s AI MicroMasters. Fast.ai’s Practical Deep Learning for Coders is also highly recommended.
- Domain-Specific Courses: For specialized fields like NLP and computer vision, consider courses like Stanford’s CS224N or DeepLearning.AI’s NLP and CV specializations. Business-oriented courses, like UC Berkeley’s AI Business Strategies, focus on implementing AI in organizations.
Certifications
In addition to courses, obtaining well-known certifications can signal your skills. Some examples:
While not all employers prioritize specific certificates, they can be a “resume booster,” showing you are serious about the field. This is especially the case with people getting into the domain. Choose certifications relevant to your desired role.
Job Market Outlook and Future Trends in AI
The AI career outlook is exceptionally promising. Demand for AI skills is booming across industries, and this trend is expected to continue well into the future:
- High Job Growth: AI roles are growing fast. U.S. jobs for computer scientists are projected to increase 26% from 2023-2033, outpacing the national average. Globally, AI specialists are in high demand as companies digitize, leading to millions of new AI jobs this decade.
- Cross-Industry Adoption: AI is expanding beyond tech, with sectors like healthcare, finance, and agriculture increasingly investing in AI. Roles like AI Product Managers and consultants are sought to guide AI integration.
- Talent Shortage and Wage Premium: There’s a shortage of AI professionals, leading to high demand and a 56% higher wage premium compared to non-AI roles. Specialists in fields like deep learning and NLP often enjoy competitive perks.
- Geographical Spread: While tech hubs remain major AI job centers, remote work is increasing global opportunities. AI job postings are spreading across new regions and cities.
- New and Emerging Roles: New AI roles like Prompt Engineer and AI Content Creator are emerging. MLOps, AI Infrastructure, and AI Ethics Officers will also grow as AI adoption expands.
Conclusion
No matter what your background is, there are a lot of job openings in the AI field for people from all fields. You can make the switch to an AI career even if you don’t have a technical background, following the pointers outlined in this article. As AI influences more and more industries, the need for skilled workers will only grow. This will create a lot of new jobs and offer a wide range of career options, which you can set yourself up for in this evolving field. By putting into use your education, getting hands-on experience, and using your domain knowledge, you can build a rewarding career in the field.
Login to continue reading and enjoy expert-curated content.






